Inspect the valve springs for breakage or corrosion and replace as necessary.
Measure the free length for conformity to specification and replace as necessary.
Limits are:
- 1.3L engine: 1.406 in. (36mm) inner; 1.539 in. (39mm) outer
- 1.5L engine 1981–82: 1.705 in. (43mm)
- 1.5L engine 1983–85: 1.654 in. (42mm)
- 1.6L engine 1986–87: 1.673 in. (42.5mm)
- 1.6L engine (non-turbo) 1988–89: 1.665 in. (42.3mm)
- 1.6L engine (turbo) 1988–89: 1.803 in. (46mm)
- 2.0L (Code MA) engine: 1.449 in. (37mm) inner; 1.469 in. (37mm) outer
- 2.0L (Code FE) engine 1983–85: 1.984 in. (50mm) outer; 1.744 in. (44mm)
inner
- 2.0L (Code FE) engine 1986–87: 2.000 in. (50mm) outer; 1.681 in. (43mm)
inner
- 2.2L engine: 1.902 in. (48mm) intake and 1.937 in. (49mm) exhaust
- 3.0L engine: 1.819 in. (46mm) intake inner and 1.988 (50.5mm) intake outer;
2.063 (52.5mm) exhaust inner and 2.264 (57.5mm) exhaust outer.
| Fig. 1: Use a caliper gauge to check the valve spring's
free length
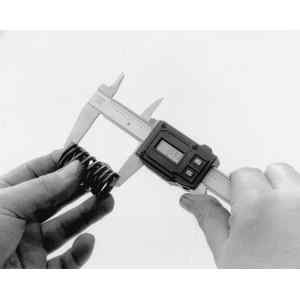
|
| Fig. 2: A carpenter's square can be used to check
the valve spring for squareness. The spring should be straight up
and down when placed like this

|
On some engines, the valve springs should also be checked for straightness.
Sit them flat next to a perpendicular surface and rotate each spring until there
is a maximum gap between the top of the spring and the perpendicular surface.
Then, measure that distance. The limits are:
- 1.6L engine 1986–87: 0.055 in. (1.4mm)
- 1.6L engine 1988–89: 0.059 in. (1.5mm)
- 2.0L (Code FE) engine: 0.066 in. (1.67mm)
- 2.2L engine: 0.067 in. (1.7mm)
- 3.0L engine: 0.064 (1.63mm) intake inner and 0.070 (1.77mm) intake outer;
0.074 (1.89mm) exhaust inner and 0.083 (2.11mm) exhaust outer